
BISON Santy
Hello, I am Santy, the funder of bisonclean.com. I have been in cleaning machinery field for more than 5 years now, and the purpose of this article is to share with you the knowledge related to pressure washer from a Chinese supplier's perspective.
Table of Contents
The pressure washer’s ability to deliver high-pressure water streams has revolutionized the cleaning process, significantly improving efficiency. As the global demand for professional cleaning solutions continues to rise, understanding the fundamental components of pressure washers, particularly their drive systems, becomes crucial for both dealers and end-users, from light household and equipment maintenance to manufacturing and construction.
A key component that significantly affects the performance and durability of a pressure washer is its drive system. It connects the engine or motor to the pump and not only determines how power is transmitted but also affects the machine’s immediate performance, maintenance requirements, operating costs, and service life.
Belt drive and direct drive pressure washers are two drive systems that dominate the market. This blog will comprehensively compare them. BISON will introduce and study their mechanical principles, performance characteristics, and practical applications to meet different user needs.
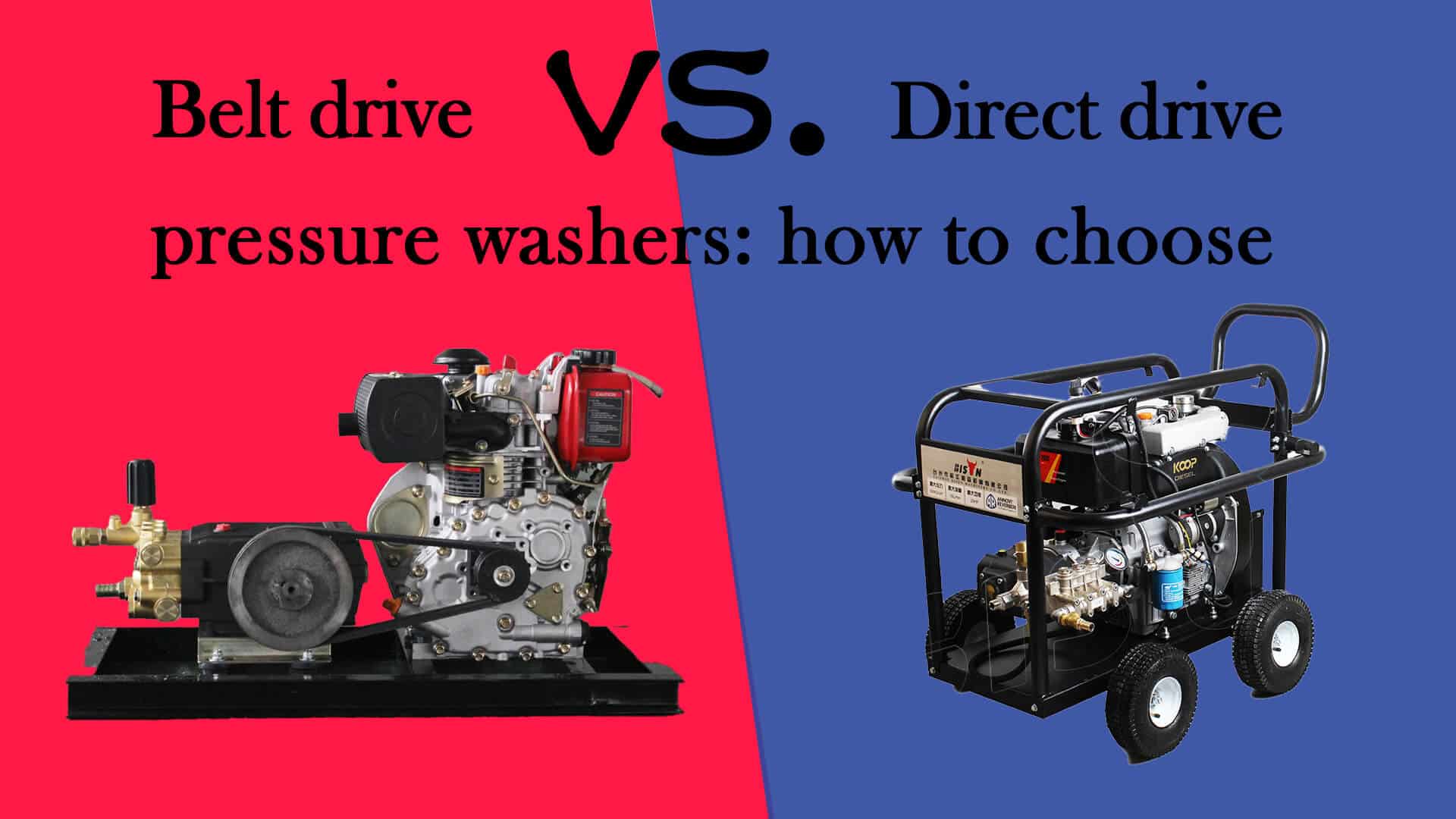
Understanding the pressure washer drive system
The drive system is a critical component of the power transmission interface between the engine (or motor) and the pump in a pressure washer. Its primary function is to transfer the mechanical energy generated by the engine to the pump, which then converts that energy into hydraulic power to produce a high-pressure water flow.
Belt drive system
The belt drive system utilizes belts and pulleys to transfer power from the engine or motor to the pump.
Its working mechanism is to utilize the engine to rotate the drive pulley, which transmits power through the belt to the driven pulley connected to the pump. This setup usually reduces the operating speed of the pump compared to the engine speed through the pulley ratio design. For example, if the engine is running at 3600 RPM, the pump may be running at 1725 RPM, depending on the pulley ratio configuration.
Direct drive system
The direct drive system uses a more direct design, with direct drive washers connecting the engine or motor directly to the pump through a solid shaft.
In this configuration, power transmission is instant and direct, with no reduction or intermediate components between the engine and the pump. The pump runs at the same speed as the engine, which for a gas engine is usually around 3400-3600 RPM.
The difference between belt drive and direct drive pressure washers
Mechanical and design comparison
Belt driven pressure washers
1.Design framework
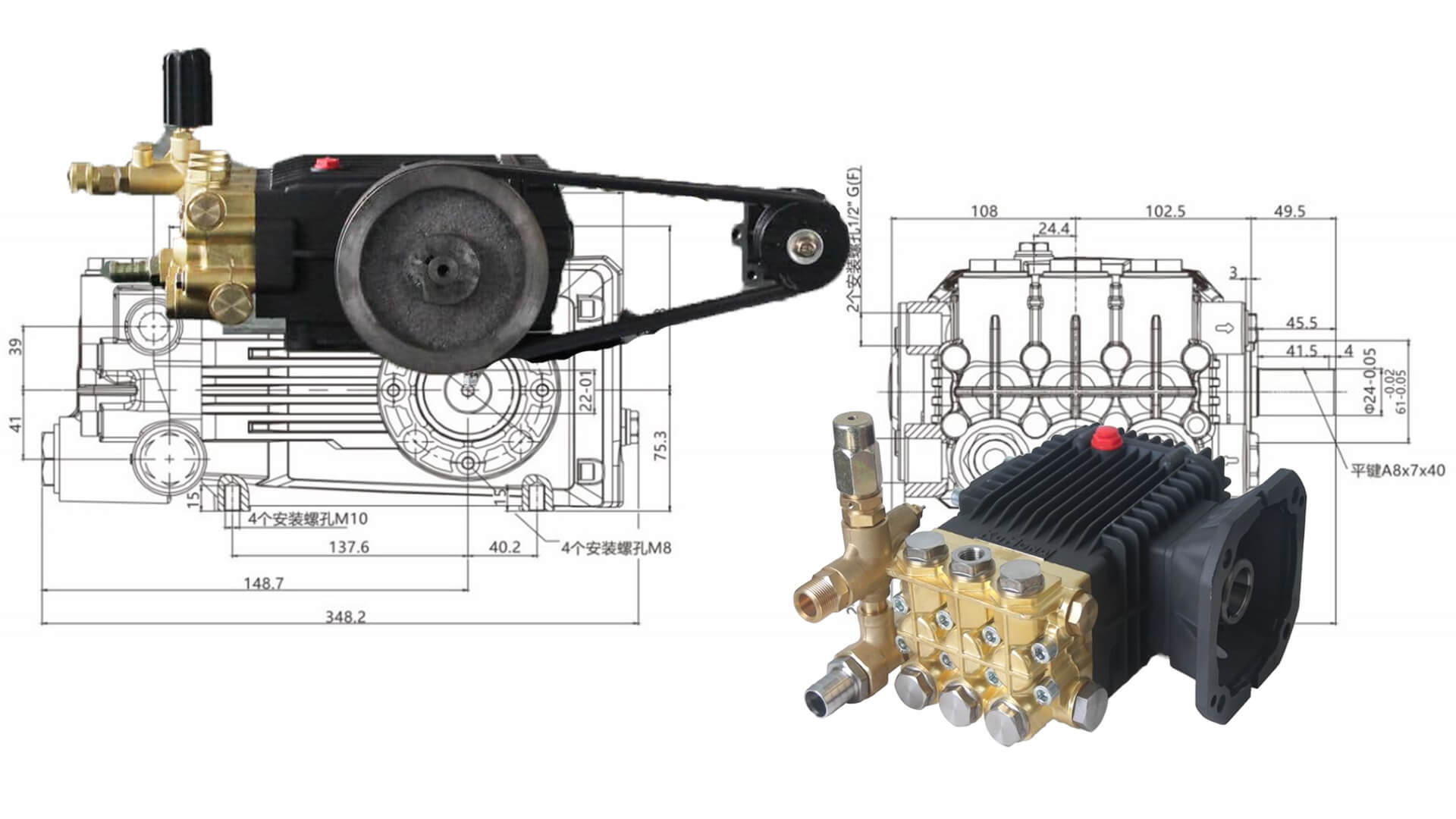
The system consists of several key components: Drive pulley, Driven pulley, V-belt or multi-groove belt, Belt tensioner, and Independent mounting positions for the engine and pump.
2.System flexibility
- Mechanical advantages: Belt-driven pressure washers offer customizable speed reduction through a selection of pulley ratios (typically 2:1). At the same time, belt elasticity acts as a built-in damping system, allowing for thermal expansion and minor misalignment.
- Operational advantages: Ability to achieve optimum pump speed independent of engine speed, providing vibration isolation between components. Belt-driven systems are able to balance minor movements during operation without stress.
3.Installation considerations
- More complex assembly process, requiring precise pulley adjustment
- Requires a strong frame design to keep components aligned
- Requires proper belt tension adjustment
Direct drive pressure washers
1.Design framework
Shaft coupling, Mounting flange, Alignment system, Compact mounting frame, and Vibration dampening elements.
2.Mechanical integration
- Direct power transmission: Immediately responds to changes in power input, with a 1:1 speed ratio between the engine and the pump. But it also generates more heat and wear than a slower-running pump in a belt-driven system.
- Constructional Efficiency: Direct-drive pressure washers have no additional components such as belts and pulleys, so they are compact, lightweight, and very portable. There are also fewer wear parts and simplified alignment requirements.
3.Considerations:
- Requires precise manufacturing tolerances
- Requires a strong shock absorption system
- Requires a rigid mounting system to prevent misalignment
- Requires an effective thermal management solution
Performance and efficiency comparison
Belt drive pressure washers
The belt system makes the machine larger and heavier, but achieves excellent vibration reduction, making pressure delivery smoother and performance more stable. The operating temperature is 20-30% lower than that of direct drive, suitable for continuous and professional use over 8 hours a day, and the highest pressure application can exceed 4000 PSI. The belt drive system can absorb vibrations and reduce noise, which is very useful in noise-sensitive environments.
Direct drive pressure washers
The power transmission efficiency of direct drive pressure washers is 98-99%, and the response to throttle changes is faster. Direct drive pressure washers are not suitable for long cleaning and are best suited for intermittent use of 2-4 hours a day because the pump exposed to the heat of the engine and running at high speed will wear quickly.
Maintenance and durability comparison
Depending on use, belt-driven pressure washers require belt tension checks every 40-50 operating hours and belt replacement every 500-1000 hours. However, their good operating temperature, vibration damping, and bearing lubrication mean less maintenance on other components such as pumps and motors. Under similar conditions, the life of the entire Belt-Driven Pressure Washer system can be 2-3 times longer than a direct drive unit.
Direct-drive pressure washers have fewer components and are easier to maintain. Basic maintenance is limited to: oil changes, seal checks, general cleaning, and basic connection checks. However, the increased pressure and temperature on the pump means more frequent repairs or replacements are required.
Cost and affordability analysis
Belt-driven pressure washers have a larger overall structure and more components, and the upfront purchase cost is usually 20-30% higher than direct drives. It is less frequently repaired, usually only the belt needs to be replaced, and the operating cost is very low compared to major component failures. They are an investment in the long-term use of heavy equipment.
Direct-drive pressure washers are more affordable to purchase. Their compact size requires less material and reduces shipping and handling costs. However, maintenance intervals are more frequent and may require replacement of the entire unit rather than repairing parts.
Belt drive vs direct drive: selection chart
The following list of guides written by BISON experts includes additional summaries of the differences between belt driven and direct driven pressure washers as well as application recommendations:
| Aspect | Belt drive pressure washers | Direct drive pressure washers |
| Operating duration | • Extended continuous operation (8+ hours) • Daily heavy use • Multiple shifts • High-frequency usage patterns | • Intermittent use (2-4 hours) • Short-term use • Periodic cleaning tasks |
| Duty cycle | • Heavy-duty cycle (90-100%) • Continuous operational capability • Minimal cooling periods required | • Medium-duty cycle (60-75%) • Regular breaks needed • More cooling periods required |
| Best suited for | • Professional cleaning contractors • Facility management services • Industrial maintenance teams • Large-scale operations | • Small business owners • Homeowners • Property maintenance • Light commercial cleaning |
| Ideal applications | • Large commercial facilities Industrial complexes • Manufacturing plants • Construction sites • Agricultural operations • Professional cleaning services • Fleet maintenance facilities • Food processing plants • Large commercial facilities | • Residential use • Small shops • Light commercial tasks • Mobile detailing services • Rental equipment • Periodic maintenance • Small retail establishments • Light-duty workshop cleaning |
Conclusion
Belt driven systems excel in professional and heavy-duty applications, while direct driven systems are compact and cost-effective in design. Both pressure washers have advantages. By understanding the differences between them in this article, you can invest in a pressure washer that offers the best performance and value.
As a leading pressure washer manufacturer in China, BISON delivers products to dealers around the world. With more than 10 years of manufacturing experience, we are able to provide innovative solutions that combine reliability, performance, and value. BISON sincerely invites global distributors to join us in taking a new step in developing their business.
You might also enjoy
Questions?
Contact Us Today.
Related Products
Find more?
Related Posts

How to clean pool tiles with a pressure washer
This comprehensive guide will walk you through the steps to restore your pool tile to its original glory using a pressure washer.

How pressure washing can help with oil field cleaning
This article will show how pressure washing can provide a cleaning solution for the oilfield industry and explore its benefits and applications.

Pressure washing vs. traditional cleaning methods
In this article, BISON will take an in-depth comparison of pressure washing vs. traditional cleaning methods to highlight their pros and cons.

Why is my pressure washer smoking
This blog will help you understand the common reasons why your pressure washer may smoke. In the end, you’ll learn what the smoke could mean






